What’s the Fuss About Organic Cotton?
What is Organic Cotton?
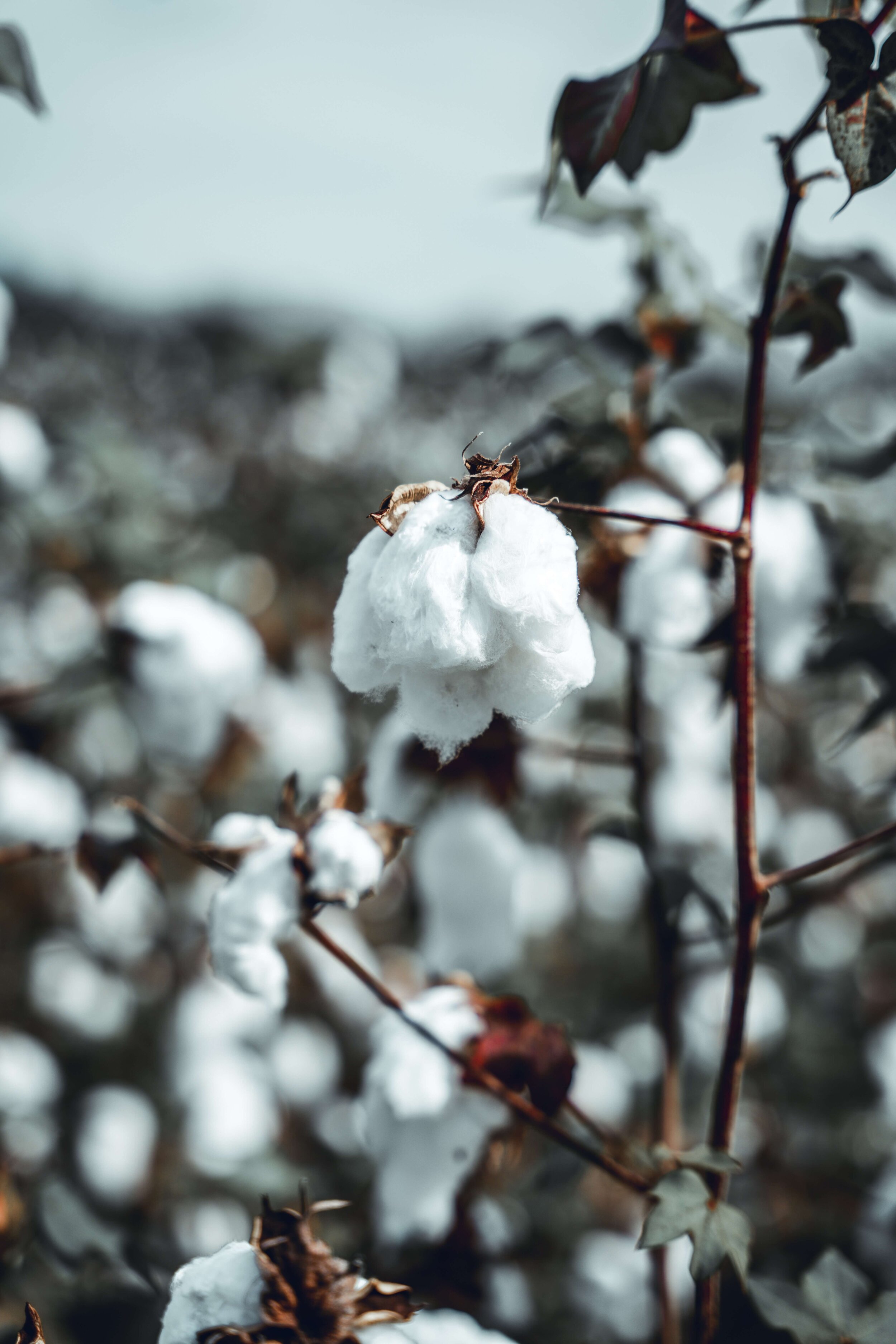
Cotton is a plant-based, biodegradable material. It could be assumed then, that it must always be sustainable. Unfortunately though, depending on how cotton is farmed, the environmental impact of the material can be significant. Producing cotton organically can be a good way to reduce cotton farming's impact.
What’s Wrong with Conventional Cotton?
Before we get into what all the fuss about organic cotton is, we need to understand some of the issues with ‘conventional cotton’. It’s important to note that cotton -- whether organic or not -- is produced differently across farms and countries, but when we talk about ‘conventional cotton’, we’re talking about the most common, average way that the fluffy plant is grown.
According to the Sustainable Apparel Coalition’s Material Sustainability Index, the environmental impact of conventional cotton production from cradle to gate (so basically, not considering cotton as a garment and its post-consumer ‘after-life’) is so significant that it’s the fifth most impactful material of all. After silk, alpaca wool, cow and goat leather, conventional cotton has the greatest eco-impact when considering global warming, eutrophication (which can lead to dead-zones), water scarcity, fossil fuels, and chemistry.
The majority of this eco-impact comes down to how thirsty conventional cotton is. You might have heard, for example, that a single conventional cotton t-shirt can require about 2,494 liters of water to make -- enough water for a person to drink 2 liters daily, over nearly three and a half years. This is a big deal, given that freshwater is essential to life on Earth and something which 1.1 billion people around the world lack proper access to, including in top cotton production countries like India.
What’s worse though, is that water isn’t just used to grow conventional cotton, but is polluted in conventional cotton production. Because of the heavy and often careless use of fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides, waterways surrounding cotton farms can become polluted with these substances, harming the health of the ecosystem and all those living in it -- humans included, when this contaminated water is drunk.
Carelessly used pesticides and herbicides in conventional cotton production can not only harm the environment, including soil health, but cotton farmers, too. In 2017, at least 50 farmers were killed in part of India, likely due to pesticide poisoning.
How is Organic Cotton Different?
Understandably, you may be looking at cotton a little differently now if you weren’t aware of this darker side of the industry. Fortunately, though, there are solutions and better ways.
Organic cotton is grown without the use of synthetic pesticides and herbicides. Organic cotton crops can be sprayed with Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) natural proteins to protect them from insect infestation and crop destruction, but not with the cocktail of toxic chemicals often sprayed over conventional cotton crops.
This not only helps to protect farmers, but the environment, too. Eutrophication occurs when water is overly enriched with nutrients, often due to fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides, which can result in dead-zones in water, where life struggles to persist. The same Sustainable Apparel Coalition data referenced earlier shows that eutrophication is reduced in organic cotton as compared to conventional cotton production.
While organic cotton, by definition, is about the use of synthetic chemicals, organic cotton often is significantly less water-intensive than conventional. Most organic cotton is just rain-fed, meaning that no additional irrigation water is added to the crops. When organic cotton isn’t rain fed, the irrigated water consumption for it is reported by Textile Exchange to be 182 liters per kg of lint (basically harvested fluff), compared to conventional cotton’s enormous 2,120 liters per kg of lint. With water scarcity being the greatest impact associated with this soft, white fiber, this is a great change.
Is All Organic Cotton the Same?
Not all organic cotton is grown equal. If we look at something like Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) certified organic cotton, we get a material that must meet ecological and social health criteria. These include wastewater treatment to prevent contamination, even by natural fertilizers, and the assurance that farmers and farmworkers are paid living wages. This is wonderful, and a great reason to look out for GOTS-certified organic cotton clothing, but the GOTS standard exists because this is not the norm in cotton production, even within organic cotton production.
Are There Any Issues with Organic Cotton?
Not even organic cotton is not free of issues. Unless organic cotton is grown within a standard like GOTS, or the Fair Trade scheme, cotton being organic does not ensure it is an ethical or wholly sustainable crop.
Organic cotton can be more land-intensive, producing less cotton per hectare than genetically modified cotton. Cotton that is genetically modified to have the Bt natural protein inside of it, rather than sprayed over it, cannot be considered organic even if no additional pesticides or herbicides are used on the crop. This Bt cotton is often more land efficient, meaning more land which can be kept natural, full of trees and life.
Because of the discrepancies in organic cotton production, certified organic cotton is a safer bet. Unless obliged to follow criteria like those in the Global Organic Textile Standard, without transparency, we can’t know that an organic cotton farm isn’t irrigating their crop with significant amounts of water or harvesting their cotton in a way that harms soil health. In this way, organic cotton can still have water scarcity and soil health impacts associated with it.
When we consider ethics, we must remember that cotton production has historically been linked to the Atlantic slave trade. Today, one in five cotton products are tied to the unjust treatment of ethnic minority groups in Xinjiang, China, where more than half a million people are forced to pick cotton. After India, China is the second-largest producer of organic cotton. This isn’t to say that cotton grown in China can never be ethical, but with little transparency in the industry, it is nearly impossible to know if non-certified organic cotton is tied to forced labor, or modern slavery.
Are There Other Types of More Sustainable Cotton?
As well as the ethical and far more sustainable organic cotton certified by GOTS or other legitimate groups, there is other more sustainably sourced cotton, too.
Australian grown cotton, for example, has reduced its use of synthetic insecticides by 97% since 1992, and the vast majority of Australian cotton growers are a part of the voluntary my Best Practice Management (myBMP) program. This program demands over 300 criteria for the more sustainable and ethical production of cotton. Such criteria include the use of rotational crops that release soil-beneficial nitrogen into the soil, like chickpeas, and criteria around water management. Australian cotton is more water-efficient than that of many other countries.
Also from Australia comes Good Earth Cotton, which is reportedly carbon positive and completely traceable from ‘seed to shelf’, thanks to FibreTrace technology. This is a fantastic step towards total ethics fashion.
Another great option is recycled cotton, which has a reduced impact compared to both conventional and organic cotton since no land is needed for agriculture, so it can be kept natural and biodiverse. It’s always good to use what we already have.
What to Buy?
If you’re looking for organic cotton, certified is the best option, especially since more supposedly ‘organic cotton’ is sold than actual organic cotton is grown, with false organic claims being made by some brands.
As always, it’s important to ask questions before you buy. Ask brands if their organic cotton is certified and with what standard. Ask where their cotton is grown, what the environmental and social impacts of their cotton production is, and how much they even know about the cotton in their garments.
Cotton is a wonderful, plant-based and biodegradable material, but we need to remember that it’s a little more complicated than that, too. Mindful purchases are always better purchases, and certifications can really help with this.
Want to Shop Organic Cotton Brands?
Here is a list of all our favorite sustainable cotton brands for the entire family!
About the Contributor
Emma Håkansson is the founder and director of Collective Fashion Justice which seeks to create a total ethics fashion system that prioritizes the life and wellbeing of non-human & human animals, as well as the planet, before profit & production. She has written countless articles on ethics, sustainability, and fashion, and has two books due out over the next two years.
MAKE SURE TO PIN THE PHOTO BELOW TO SAVE THIS POST FOR LATER!
WANT TO FIND SUSTAINABLE BRANDS? Visit Our Brand Directory!
Our Brand Directory is home to hundreds of sustainable brands, from makeup to cleaning supplies, from underwear to shoes. We have broken everything down by category for easy shopping, along with discount codes unique to Sustainably Chic viewers.